Page 6 - MGMA MRM issue 02
P. 6
Make the Very Low A building may have a time period allowed for a rainfall intensity in l/ (s.m2). There are graphs
the replacement/refurbishment of sheeting and
for one year, five years, 50 years and 500 years
Calculated rooflights of only 20 years, but in most cases, in the standard, and also a more complex
procedure which allows rainfall intensity to be
it would not be acceptable to flood the building
contents once every 20 years. Conversely, a
calculated for any return period. Most calculation
building where the construction materials have software will use this more complex procedure.
Choice a very long expected lifespan, but where the The graphs are not very detailed, so some
interpolation will be needed, both to locate the
contents of the building have no real value,
may have a protection life much shorter than a site and then work out the rainfall intensity.
theoretical building component’s life.
The rainfall intensity can then be multiplied by
The only logical approach is to determine how a catchment area to get a flow rate in l/s, which
often it would be acceptable for the building can be compared to manufactured capacities, or
to flood and then to use that value. Too short used for more complex detailed design. Selecting
Medium and the occupiers will be disadvantaged; too the correct rainfall intensity is critical to the
long and the system will be uneconomic. For a design process, and effort expended at this early
building of normal use, 60 years at Category 2 stage, will help ensure the correct design later on
protection is a suitable level of protection. in the process.
It could be argued that Category 4 is the best The MGMA has produced an eaves gutter design
Low design level to use in all cases, as it will never flow chart GD18 Eaves gutter design flow which
The UK climate is becoming warmer, wetter and
windier and extreme weather is now an all-year- flood. This is technically correct, however there enables the user to perform calculations to BS
round probability in the UK, ranging from flash must always be a balance between protection EN12056-3:2000. By entering simple information
floods one day to heat waves the next. and cost. relating to building dimensions, geographical
location and proposed gutter style, the flow chart
Climate change is one of the key drivers for Category 4 is likely to give figures 2.5 times will provide guidance on gutter specification.
improving roof drainage and water management. higher than a rainfall intensity derived from a The flow chart is available for download on the
Developing new standards, regulations and realistic protection life, which on some buildings MGMA web site.
testing methods to ensure products and may make it impossible to drain, on others very
solutions align to the worst-case scenarios of difficult, and on all, more costly. There is a more It is important that rainwater manufacturers offer
climate models is essential. serious issue with the use of Category 4 when the relevant support and technical advice to their
High applied to siphonic drainage, as there is a risk specifier and installer customers so that metal
Rainwater systems are integral to protecting the systems will clog up before they ever really rainwater gutters are correctly specified across
our buildings and channelling water from roof to function siphonically. all projects. MGMA members can advise on
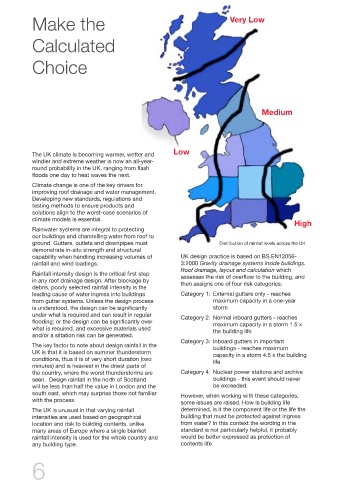
ground. Gutters, outlets and downpipes must Distribution of rainfall levels across the UK design to BS EN12056-3:2000; further advice
demonstrate in-situ strength and structural Siphonic systems are laid level and rely on and guidance is available from any MGMA
capability when handling increasing volumes of UK design practice is based on BS EN12056- regular flushes of high velocity flow to stay clear. member company whose details can be found on
rainfall and wind loadings. 3:2000 Gravity drainage systems inside buildings. If the systems are designed to Category 4, then the MGMA website at www.mgma.co.uk
Roof drainage, layout and calculation which it may be 600 years or more between flushes
Rainfall intensity design is the critical first step assesses the risk of overflow to the building, and through, by which time they will have clogged up.
in any roof drainage design. After blockage by then assigns one of four risk categories:
debris, poorly selected rainfall intensity is the Once a building protection life has been Selecting the correct rainfall is essential
leading cause of water ingress into buildings Category 1: External gutters only - reaches obtained, the graphs in the national annex of
from gutter systems. Unless the design process maximum capacity in a one-year BS EN12056-3:2000 can be used to determine
is understood, the design can be significantly storm
under what is required and can result in regular Category 2: Normal inboard gutters - reaches
flooding; or the design can be significantly over maximum capacity in a storm 1.5 x Damage caused by inadequate roof drainage
what is required, and excessive materials used the building life
and/or a siltation risk can be generated.
Category 3: Inboard gutters in important
The key factor to note about design rainfall in the buildings - reaches maximum
UK is that it is based on summer thunderstorm capacity in a storm 4.5 x the building
conditions, thus it is of very short duration (two life
minutes) and is heaviest in the driest parts of
the country, where the worst thunderstorms are Category 4: Nuclear power stations and archive
seen. Design rainfall in the north of Scotland buildings - this event should never
will be less than half the value in London and the be exceeded.
south east, which may surprise those not familiar However, when working with these categories,
with the process. some issues are raised. How is building life
The UK is unusual in that varying rainfall determined, is it the component life or the life the
intensities are used based on geographical building that must be protected against ingress
location and risk to building contents, unlike from water? In this context the wording in the
many areas of Europe where a single blanket standard is not particularly helpful, it probably
rainfall intensity is used for the whole country and would be better expressed as protection of
any building type. contents life.
6 7